User
For more information about the features available to user-level accounts, please see the Account levels article.
Creating a user
- Log in to ispmanager with a reseller-level account or above.
- Navigate to the Users section.
- Click
 Add a user on the toolbar.
Add a user on the toolbar. Follow the steps below.
Step 1. Main settings
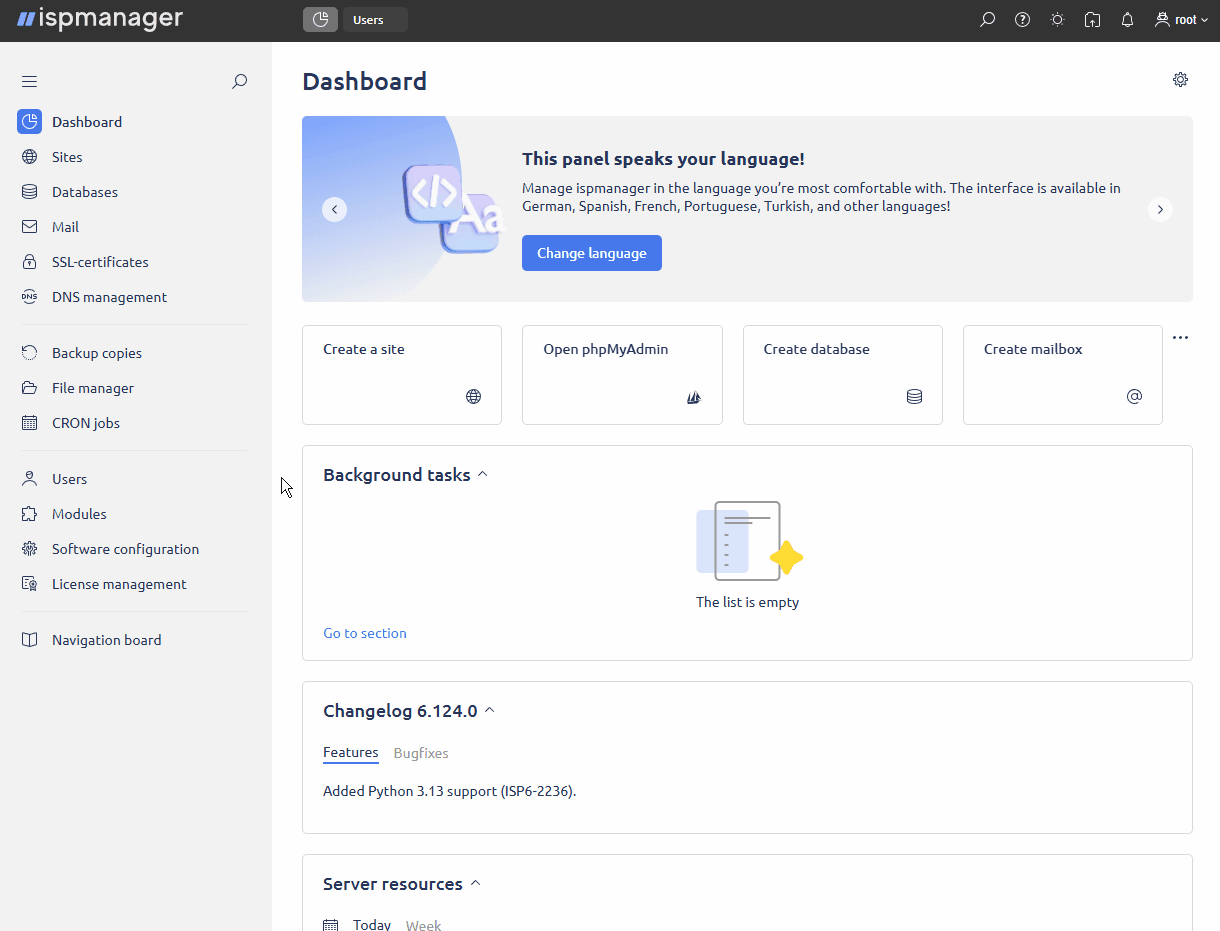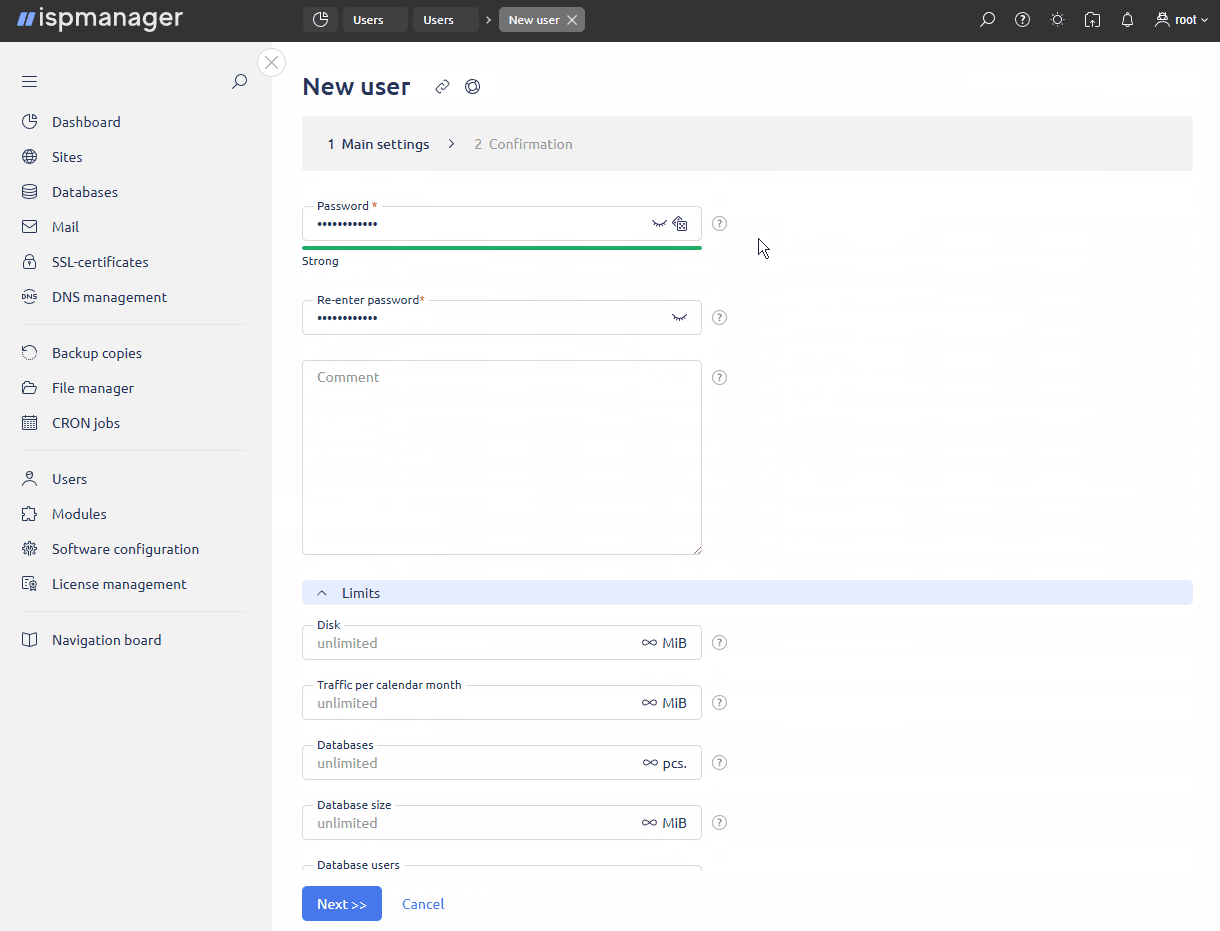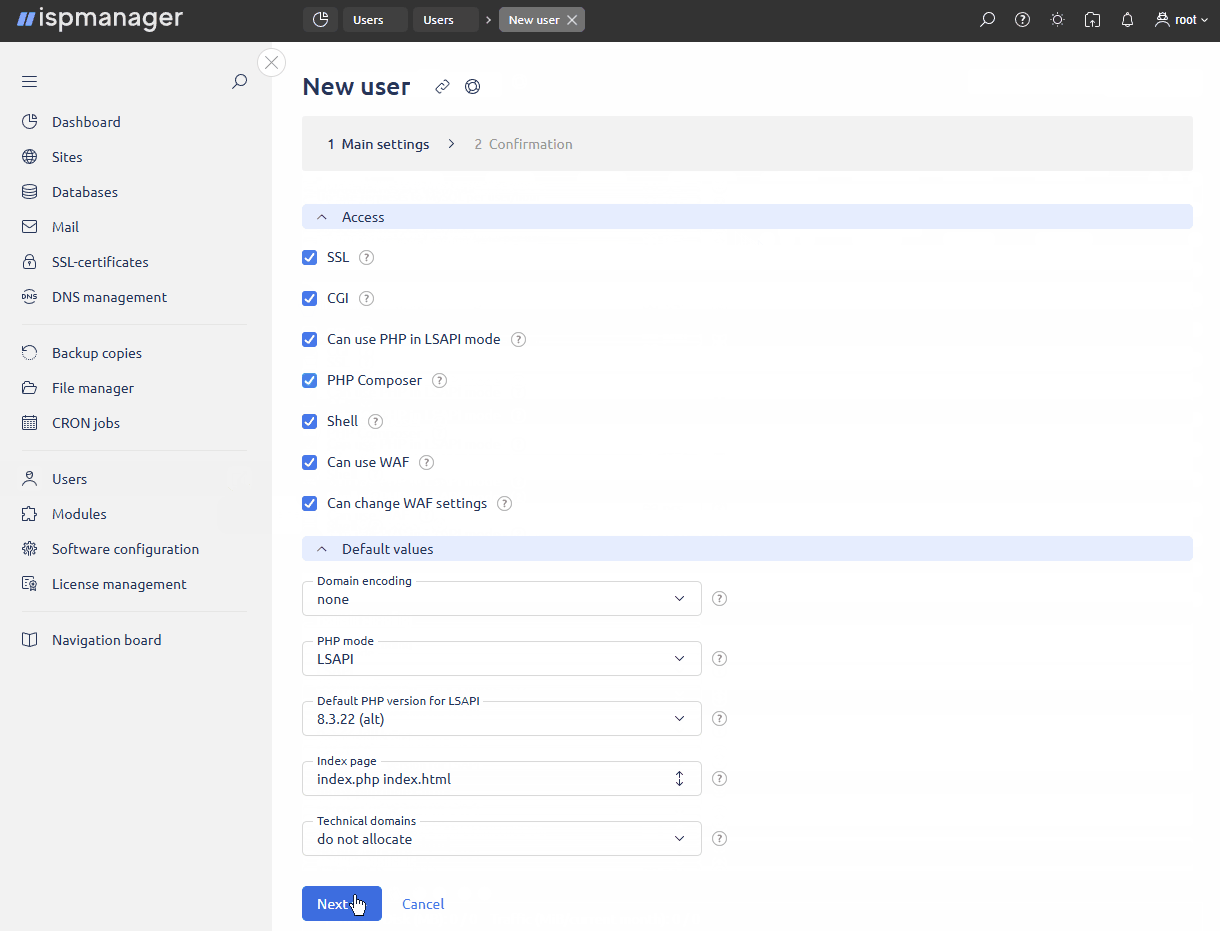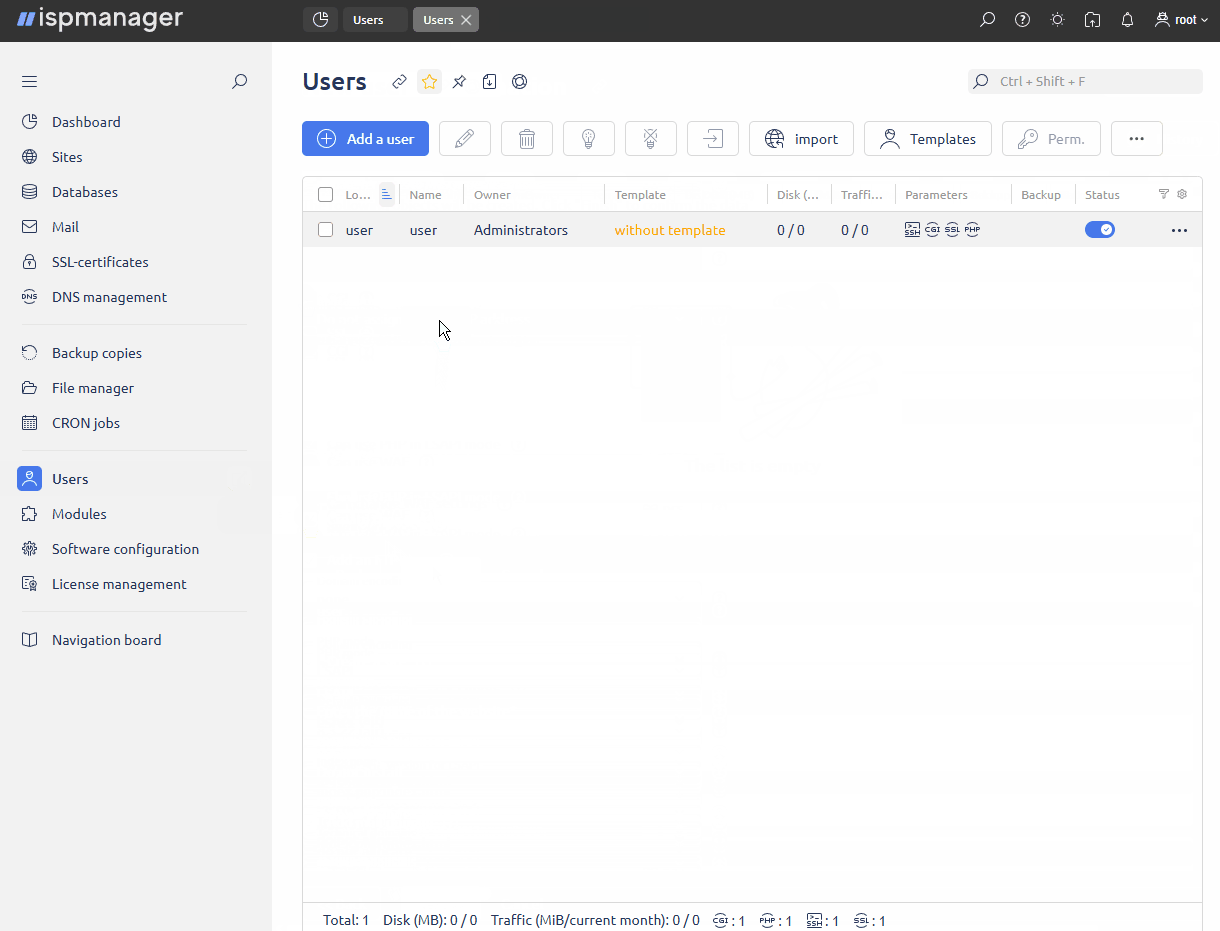
In the Main settings block, specify general information about the user:
- Login — username for logging into the ispmanager panel and shell. Only ASCII printable characters are allowed. Maximum length: 32 characters.
- Name — full name of the user or any other name. Identifies the client in the panel. The information is displayed only for administrators in the Users section → the Name column.
Owner — reseller or administrator who will manage the user. The field is only available in ispmanager host.
The user's owner can not be changed after the user is created.
- Template — automatically transfers user settings from a template. The settings can be overwritten manually.
- Password — password to log in to the panel. Only ASCII printable characters are allowed. Maximum length: 128 characters.
- Re-enter password — enter the password once again to verify it is correct.
- Comment — a note, a description, or any other text.
- Backups — adds the user to the periodic backup list and allows the user to create user backups. If the box in unchecked, backups will not be created for this user automatically.
In the Limits block, specify user limits on allowed panel parameters. By default, no limits are set.
In the Resources block, specify user limits on the server resource usage. By default, no limits are set.
Resource settings are only available in ispmanager host.
In the Access block, specify the software that will be available to the user:
Access settings are only available to accounts with superuser rights.
- SSL — allows installation of SSL certificates for websites.
- CGI — allows using CGI scripts for websites.
- PHP as Apache module — allows the user to create websites with PHP as Apache module. The field is available if Apache MPM-Prefork/Apache MPM-ITK and PHP module are installed.
- PHP as CGI — allows the user to create websites with PHP as CGI. The field is available if Apache MPM-Prefork or Apache MPM-ITK is installed.
- PHP as FastCGI (Apache) — allows the user to create websites with PHP as FastCGI (Apache). The field is available if Apache MPM-Prefork and PHP module are installed.
- PHP as FastCGI (Nginx + PHP-FPM) — allows the user to create websites with PHP as FastCGI (Nginx + PHP-FPM). The field is available if Nginx and PHP-FPM FastCGI are installed.
- PHP in LSAPI mode — allows the user to create websites with PHP in LSAPI mode. The field is available if OpenLiteSpeed or LiteSpeed is installed.
- PHP Composer — allows the user to manage PHP packages using PHP Composer. The field is available if PHP Composer is installed.
- Node.js — allows the user to create websites with Node.js. The field is available if Nginx and Node.js are installed.
- Python — allows the user to create websites with Python. The field is available if Nginx and Python are installed.
- Shell — allows the user to use the panel's shell client and log in to the server via SSH.
In the Default values block, specify the settings that will be used as defaults when the user creates new websites:
- Domain encoding — encoding used for the user's websites:
- not specified — encoding from the web server settings will be used
- UTF-8 — UTF-8 encoding will be used
- PHP handler type — a handler type for the user's websites. The field is available if at least one of the PHP handlers is enabled for the user.
- PHP version (LSAPI module) by default — the PHP version for the user's websites with the PHP as LSAPI handler. The field is available if PHP in LSAPI mode is enabled for the user. PHP versions are available for selection if they are installed and LSAPI is allowed for them.
- PHP version (CGI) by default — the PHP version for the user's websites with the PHP as CGI handler. The field is available if PHP as CGI or PHP as FastCGI (Apache) is enabled for the user. PHP versions are available for selection if they are installed.
- PHP version (PHP-FPM) — the PHP version for the user's websites with the PHP as PHP-FPM handler. The field is available if PHP as FastCGI (Nginx + PHP-FPM) is enabled for the user. PHP versions are available for selection if they are installed and PHP-FPM is allowed for them.
- PHP version (Apache module) by default — the PHP version for the user's websites with PHP as Apache module. The field is available if PHP as Apache module is enabled for the user. PHP versions are available for selection if they are installed and Apache module is allowed for them.
- Node.js version by default — the Node.js version for the user's websites with Node.js. The field is available if Node.js is enabled for the user.
- Python version by default — the Python version for the user's websites with Python. The field is available if Python is enabled for the user. Python versions are available for selection if they are installed and allowed for use.
Index page — the address of a starting page for the user's websites. The index page will open every time the user tries to access the domain's root URL. You can specify multiple URLs names in order of descending priority, separated by spaces. If the first specified page does not exist, the system will check for the existence of the second page, and so on. The default value is index.html.
ExampleIf index.html is specified as the index page, requests to example.com will be redirected to https://example.com/index.html.
- Technical domain — the technical domain that will be assigned to the user's websites. The field is only available in ispmanager host. Only the technical domains that belong to the user's owner are available for selection.
Click Next.
Step 2. Additional information
In the Select IP address block, set an IP address for the user. After the user is created, their IP address can be changed in the IP addresses section.
- IPv4 allocation type:
- Do not assign a private IP address — the user will be created without a dedicated IPv4 address.
- Automatically — the user will be automatically assigned a free IP address.
- From the subnet — the user will be automatically assigned a free IP address from the selected subnet.
- Allocate manually:
- IPv4 address — user IP address in the format: 123.456.789.000. Works only with NAT.
- IPv6 allocation type:
- Do not assign a private IP address — the user will be created without a dedicated IPv6 address.
- Allocate manually:
- IPv6 address — user IP address in the format: 2001:0db8:abf2:29ea:5298:ad71:2ca0:4ff1. Works without NAT.
In the Create automatically block, specify the entities that will be created with the user:
- Create the selected objects automatically — allows creation of additional entities of the user.
- Add an FTP user — allows creation of a new FTP user.
- Name of the FTP user — name of the user with access to the FTP server, for example ftp_user. Only ASCII printable characters are allowed. Maximum length: 64 characters.
- Create a site — allows creation of a new site.
- Name of the site — domain name of the site, for example example.com.
- Select a script — web script for installing CMS or CRM for the website.
- IP addresses — the IP addresses that will be assigned to the website. The field is only available in ispmanager lite.
- Create a mail domain — allows creation of a new mail domain.
- Name of the mail domain — mail domain name, for example: mail-example.com.
- IP address — the IP address that will be used for mail. The field is only available in ispmanager lite.
Click Next.
Step 3. Confirmation
At the Confirmation step, a list of entities that will be created is generated.
- User
- FTP user
- Website
- Mail domain
Click Finish to create them.
Actions with the user
- Log in to ispmanager with a reseller-level account or above.
- Navigate to the Users section or select a user from the list.
- The following actions are available on the toolbar:
| Button | Description |
|---|---|
 | Change user account settings |
 | Delete user |
 | Enable user |
 | Disable user |
 | Log in to the account with user rights |
| Import user | |
| Create a user template | |
 | Configure access to functions |
| View user history of changes | |
| Transfer data between users |
Creating user account templates
Templates allow setting default values for the user creation form. Templates are convenient for creating users with similar permissions, for example, when creating a user based on a hosting plan.
- Log in to ispmanager with a reseller-level account or above.
- Navigate to the Users section.
- Click
 Templates on the toolbar.
Templates on the toolbar. - Click
 Create a template on the toolbar or
Create a template on the toolbar or  Edit an existing one.
Edit an existing one. - Specify the name of the template.
- If necessary, configure values in the Limits, Resources, Access and Default values sections.
- Save the changes.
User skeleton directories
Skeleton directories will be automatically recreated in the home directories of new users.
To create a skeleton directory:
- Log in to ispmanager with superuser rights.
- Navigate to the File manager.
- Go to the
/usr/local/mgr5/etc/directory → create auser.skelfolder. - Add the necessary files.
- Restart the panel.
- Connect to the server via SSH.
Restart the panel by running the following command in the terminal:
pkill core- Return to the panel by the link:
https://IP_ADDRESS:1500/ispmgr.
System user identifiers
By default, the control panel creates user accounts with UID and GID numbers starting with 1010. The first user will be created with UID and GID 1010, the second one will have the 1011 UID and GID, and so on.
Changing the IDs of existing users may cause control panel malfunction.
If necessary, change the UID and GID values for new users:
Add the following parameters to the control panel configuration file
/usr/local/mgr5/etc/ispmgr.conf:MinGID 1100 MinUID 1100DetailsMinGID — minimum GID value
MinUID — minimum UID value
Restart the control panel.
Details- Connect to the server via SSH.
Restart the panel by running the following command in the terminal:
pkill core- Return to the panel by the link:
https://IP_ADDRESS:1500/ispmgr.