Account limits and resources
ispmanager provides flexible distribution of server resources for each user. This ensures effective load management and helps maintain system stability. For example, you can adjust:
- amount of RAM allowed for use
- number of running processes per user
- maximum size of a mailbox or allocated disk space
- number of available Apache handlers for a site, etc.
Managing limits and resources
The values are applied to all users of the reseller.
The reseller settings specify 10 mailboxes. This means all users of this reseller can create 10 mailboxes in total.
How it works:
- user1 created 5 mailboxes out of 10.
- user2 created 3 mailboxes out of 10.
- user3 created 2 mailboxes out of 10.
- user4 cannot create any mailboxes because the specified limit in the reseller settings has been reached.
To let user4 create a new mailbox, you need to increase the limit value in the reseller settings.
- Log in to the ispmanager panel with an administrator-level account or above.
- Navigate to the Resellers section.
- Click
 Add a reseller on the toolbar or
Add a reseller on the toolbar or  Edit an existing one.
Edit an existing one. - Specify the required Limits and Resources.
- Save the changes.
- Log in to the ispmanager panel with a reseller-level account or above.
- Navigate to the Users section.
- Click
 Add a user or
Add a user or  Edit an existing one.
Edit an existing one. - Specify the required Limits and Resources.
- Save the changes.
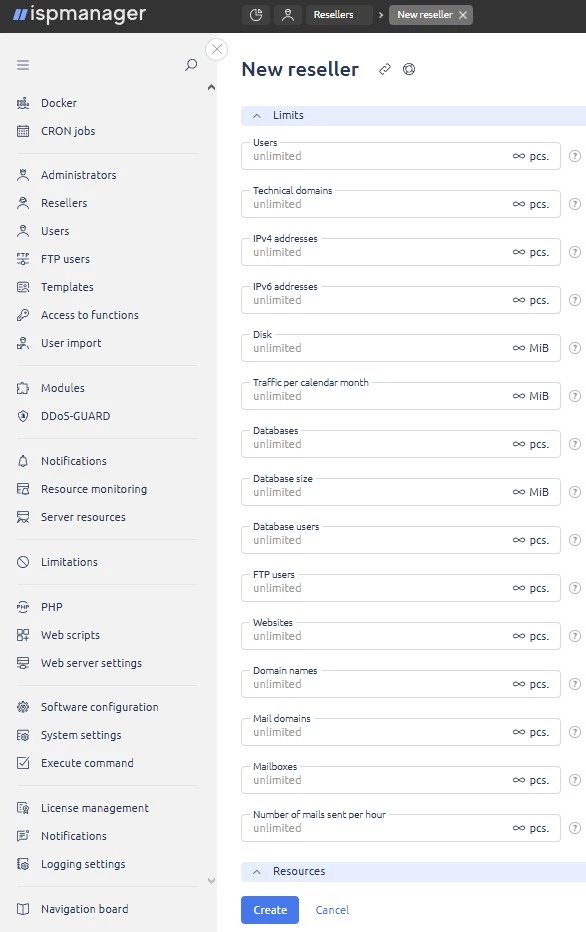
Limits
- Users — the maximum number of users the reseller can create.
- Technical domains — the maximum number of technical domains the reseller can create.
- IPv4 addresses — the maximum number of IPv4 addresses that can be assigned to the reseller by an administrator for creating subnets.
IPv6 addresses — the maximum number of IPv6 addresses that can be assigned to the reseller by an administrator for creating subnets.
DetailsThe Users, Technical domains, IPv4 addresses and IPv6 addresses fields are only available in reseller settings.
When the limits are reached, the system will show a notification and the reseller will not be able to create new users, technical domains, and IP addresses.
Disk — maximum available disk space for user data, does not apply to databases. This field is available if disk quotas are enabled.
DetailsThe limit only applies to web servers. If the disk space is occupied to its full capacity, new data will not be written.
The limits apply to individual user files and do not affect system files.
Traffic per calendar month — maximum available traffic for sites and FTP users per a calendar month. The field is available if resource usage statistics is enabled.
DetailsThe field is created to manage hosting services from the billing system. Without integration with the billing system, the limit will not be applied.
When the limit is reached, the service in the billing system for the user will be suspended. To continue using the service, the user will need to renew the subscription.
Parameter of the "userprops" table:
- limit_traff — user traffic limit. The setting is available to accounts with superuser rights.
Databases — the maximum number of databases the user(s) can create.
DetailsWhen the limit is reached, the system will show a notification and the user(s) will not be able to create new databases.
Database size — maximum available disk space for all databases of the user(s). The field is only available in ispmanager host.
DetailsParameter of the "userprops" table:
- limit_db_size — database size limit. The check_limit_dbsize periodic function checks the size of the user's databases against the limit, if specified, every 10 minutes. When the limit is reached, the user(s) will not be able to edit database users and add new information. The setting is available to accounts with superuser rights.
Database users — the maximum number of database users the user(s) can create.
DetailsWhen the limit is reached, the system will show a notification and the user(s) will not be able to create new database users.
FTP users — the maximum number of FTP users the user(s) can create.
DetailsWhen the limit is reached, the system will show a notification and the user(s) will not be able to create new FTP users.
Websites — the maximum number of sites the user(s) can create.
DetailsWhen the limit is reached, the system will show a notification and the user(s) will not be able to create new sites.
Domain names — the maximum number of domain names the user(s) can create.
DetailsWhen the limit is reached, the system will show a notification and the user(s) will not be able to create new domains.
Mail domains — the maximum number of mail domains the user(s) can create.
DetailsWhen the limit is reached, the system will show a notification and the user(s) will not be able to create new mail domains.
Mailboxes — the maximum number of mailboxes the user(s) can create.
DetailsWhen the limit is reached, the system will show a notification and the user(s) will not be able to create new mailboxes.
Number of mails sent per hour — the maximum number of emails the user(s) can send from each of their mailbox within 1 hour. If the field value is set to 1, all outgoing emails will be blocked. The value can be overridden at the mailbox level. If the field is left blank, the mail server limit will apply.
DetailsWhen the limit is reached, the system will show a notification and the user(s) will not be able to create and send any emails.
Parameter of the "userprops" table:
limit_mailrate — limit on the number of emails sent. Exim tracks the number of emails and blocks new sendings if the limit is reached. The setting is available to accounts with superuser rights.
Configuration file:
- Debian-based operating systems:
/etc/exim4/ratelimits RHEL-based operating systems:
/etc/exim/ratelimitsThe file contains limits in the format: MAILBOX_NAME:LIMIT_VALUE.
Resources
Resource management is only available in ispmanager host.
If the sites do not use Nginx or Apache, but these web servers are installed in the panel, the specified limits will still apply.
CPU time — the maximum duration of each process execution of the user(s) in seconds. This field is available if the Apache web server is installed. The parameter affects child processes, CGI scripts, and SSI commands, but does not affect the web server itself.
DetailsParameter of the "userprops" table:
- limit_cpu — CPU time limit. The limit is set at the Apache level for processes that are launched through the web server. The setting is available to accounts with superuser rights.
Configuration files:
- Debian-based systems:
/etc/apache2/users-resources/USERNAME/vhost.conf - RHEL-based systems:
/etc/httpd/conf/users-resources/USERNAME/vhost.conf
This file contains the RLimitCPU VALUE parameter, where VALUE is the value of the CPU time limit.
- Debian-based systems:
/etc/apache2/users-resources/USERNAME/php5_module.conf - RHEL-based systems:
/etc/httpd/conf/users-resources/USERNAME/php5_module.conf
This is the configuration file for the PHP module which contains the php_admin_value max_execution_time VALUE parameter, where VALUE is the value of the CPU time limit.
RAM — the limit on RAM usage for each process of the user(s), specified in MB. The field is available if the Apache web server is installed. The parameter affects child processes, CGI scripts, and SSI commands, but not the web server itself.
DetailsParameter of the "userprops" table:
- limit_memory — RAM limit. The limit is set at the Apache level for processes that are launched through the web server. The setting is available to accounts with superuser rights.
Configuration files:
- Debian-based systems:
/etc/apache2/users-resources/USERNAME/vhost.conf - RHEL-based systems:
/etc/httpd/conf/users-resources/USERNAME/vhost.conf
This file contains the RLimitMEM VALUE parameter, where VALUE is the value of the RAM limit.
- Debian-based systems:
/etc/apache2/users-resources/USERNAME/php5_module.conf - RHEL-based systems:
/etc/httpd/conf/users-resources/USERNAME/php5_module.conf
This is the configuration file for the PHP module which contains the php_admin_value memory_limit VALUE parameter, where VALUE is the value of the RAM limit.
User processes — the maximum number of processes the user(s) can run. This field is available if the Apache web server is installed. This parameter affects child processes, CGI scripts, and SSI commands, but not the web server itself.
DetailsParameter of the "userprops" table:
- limit_process — limit on the number of user processes. The setting is available to accounts with superuser rights.
- Debian-based systems:
/etc/apache2/users-resources/USERNAME/vhost.conf - RHEL-based systems:
/etc/httpd/conf/users-resources/USERNAME/vhost.conf
This file contains the RLimitNPROC VALUE parameter, where VALUE is the value of the user processes limit.
Mailbox size — the maximum size of each mailbox of the user(s).
DetailsParameter of the "userprops" table:
- limit_email_quota — limit on the maximum mailbox size. The limit is set for each mailbox using the email.edit event. After that, the data is passed to Dovecot and Exim. If a mailbox size reaches the specified limit, emails are blocked by Exim. The setting is available to accounts with superuser rights.
Cron jobs — the maximum number of scheduler tasks available.
DetailsParameter of the "userprops" table:
- limit_scheduler — limit on the number of scheduler jobs. The limit is monitored by the scheduler.edit event. The setting is available to accounts with superuser rights.
Simultaneous connections per session from one IP — the maximum number of concurrent connections from one IP address to the site. The field is available if the Nginx web server is enabled.
DetailsParameter of the "userprops" table:
- limit_nginxlimitconn — limit on the number of simultaneous connections per session. Limits are specified at the Nginx level. The setting is available to accounts with superuser rights.
Configuration files:
/etc/nginx/conf.d/ispresources.conf— the file sets a new memory zone with connection data. The more concurrent connections are allowed, the more memory is allocated./etc/nginx/users-resources/USERNAME/connlimit.conf— the file contains the exact number of connections. If their limit is exceeded, the web server will ignore all exceeding connections.
Apache handlers for each site — the maximum number of Apache handlers available for each enabled site. This field is available if the Apache web server with the ITK module is enabled.
DetailsParameter of the "userprops" table:
- limit_maxclientsvhost — limit on the number of Apache handlers. The setting is available to accounts with superuser rights.
Configuration file:
- Debian-based systems:
/etc/apache2/users-resources/ИМЯ_ПОЛЬЗОВАТЕЛЯ/vhost.conf - RHEL-based systems:
/etc/httpd/conf/users-resources/ИМЯ_ПОЛЬЗОВАТЕЛЯ/vhost.conf
This file contains the MaxClientsVHost VALUE parameter, where VALUE is the value of the limit on the number of Apache handlers.
- Simultaneous MySQL connections per user — the maximum number of concurrent connections between MySQL and each MySQL user.
- MySQL connections per user/hour — the maximum number of new connections between MySQL and each MySQL user within 1 hour.
- MySQL queries per user/hour — the maximum number of commands that can be executed by each MySQL user in 1 hour.
MySQL UPDATE queries per user/hour — the maximum number of data-modifying commands that can be executed by each MySQL user in 1 hour.
DetailsLimits on Simultaneous MySQL connections per user, MySQL connections per user/hour, MySQL queries per user/hour, and MySQL UPDATE queries per user/hour are set at the MySQL level for each database user, for both native and alternative DBMSs, including remote connections.
Parameter of the "userprops" table:
- limit_mysql_maxuserconn — limit on the number of simultaneous MySQL connections.
- limit_mysql_maxconn — limit on the number of MySQL connections.
- limit_mysql_query — limit on the number of queries to MySQL.
- limit_mysql_update — limit on the number of UPDATE queries to MySQL.
The setting is available to accounts with superuser rights.

Viewing resources and limits
The user and the reseller can view their available and used resources and limits on the dashboard in the Limits block.
Differences between ispmanager business and host
| Limits | Business | Host |
| Debian-based systems:
RHEL-based systems: | Debian-based systems:
RHEL-based systems: |
| Simultaneous connections per session | /etc/nginx/vhosts-resources/USERNAME/ | /etc/nginx/users-resouces/USERNAME/ |